-
Photocatalytic CO2 reduction by Cr-substituted Ba2(In2-xCrx )O5 ·(H2O)δ (0.04 ≤ x ≤ 0.60)
S. Yoon, M. Gaul, S. Sharma, K. Son, H. Hagemann, D. Ziegenbalg, U. Schwingenschlogl, M. Widenmeyer and A. Weidenkaff
Solid State Sciences, in press (2018)


DOI:10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2018.02.005 | Abstract
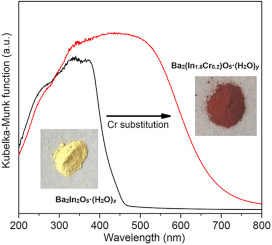
Cr-substituted polycrystalline Ba2(In2-xCrx)O5·(H2O)δ powders (0.04 ≤ x ≤ 0.60) were synthesized by solid state reaction to investigate the relation of crystal structure, thermochemical, magnetic, and optical properties. The Cr-substitution results in an unit cell expansion and formation of the higher-symmetric tetragonal phase together with increased oxygen and hydrogen contents. Magnetic property measurements reveal that the diamagnetic pristine Ba2In2O5·(H2O)δ becomes magnetically ordered upon Cr-substitution. By UV–vis spectroscopy a gradual shift of the absorption-edge energy to lower values was observed. Numerical calculations showed that the observed bandgap narrowing was ascribed to the Cr induced states near the Fermi level. The correlation between the changes of crystal chemistry, magnetic, and optical properties of Cr-substituted Ba2(In2-xCrx)O5·(H2O)δ can be explained by the replacement of In by Cr. Consequently, an enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity was observed with increasing Cr substitution, compatible with the state-of-the-art high surface area TiO2 photocatalyst (P-25).